Influence of Sunlight on Insomnia and Circadian Rhythms
The Role of Daylight in Affecting Human Circadian Rhythms Despite Modern Living Conditions
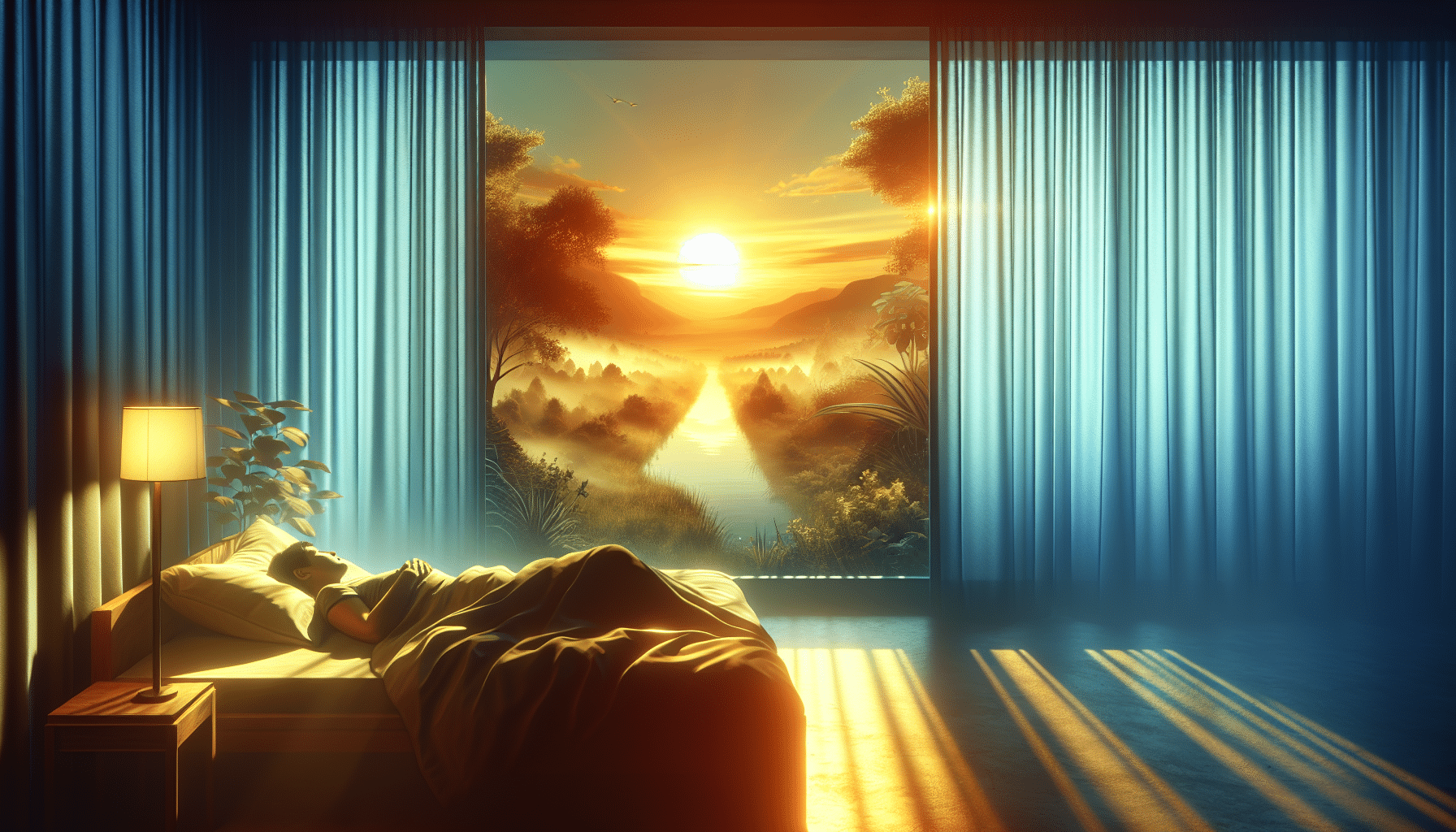
In today’s world, where artificial lighting and indoor living are prevalent, it might seem that sunlight’s influence on our sleep patterns has diminished. However, research from the University of Michigan reveals that our circadian rhythms remain deeply connected to natural light cycles. Despite the conveniences of modern life, daylight continues to play a crucial role in regulating our internal clocks. According to study author Ruby Kim, a U-M postdoctoral assistant professor of mathematics, “Humans really are seasonal, even though we might not want to admit that in our modern context.” This research highlights how our physiology is still influenced by the amount of sunlight we receive, affecting how we adjust to changes in our daily schedules.
Insights from the University of Michigan Research on Seasonal Changes and Sleep Patterns
The University of Michigan study sheds light on how seasonal changes impact sleep patterns. By analyzing sleep data from thousands of individuals using wearable health devices, researchers discovered that circadian rhythms are tuned into the seasonality of sunlight. Participants, who were medical residents with varying schedules, demonstrated a seasonal dependence in their circadian rhythms. This finding underscores the hardwired nature of this feature in humans. The study, published in the journal *npj Digital Medicine*, provides strong evidence that our circadian clocks are not singular but rather consist of two interacting components: one tracking dawn and the other dusk. This dual-clock system reflects our evolutionary history of adapting to natural light cycles.
Insomnia, Seasonal Affective Disorder, and Mental Health
Connection Between Circadian Rhythms and Seasonal Affective Disorder
The research from the University of Michigan also offers valuable insights into the connection between circadian rhythms and seasonal affective disorder (SAD). SAD is a type of depression linked to seasonal changes, particularly the reduced daylight during winter months. The study suggests that our biologically hardwired seasonal timing affects how we adjust to changes in our daily schedules, potentially influencing the onset of SAD. Understanding this connection could pave the way for new approaches to diagnosing and treating SAD by aligning sleep schedules with natural circadian rhythms.
Potential Implications for Mood, Anxiety, and Other Mental Health Issues Related to Insomnia
Beyond SAD, the study’s findings have broader implications for mental health. Researchers, including the study’s senior author Daniel Forger, have shown that mood and anxiety disorders are strongly affected by the alignment of sleep schedules with circadian rhythms. Disruptions in this alignment can exacerbate mental health issues, highlighting the importance of maintaining a regular sleep-wake cycle. The study’s insights into the genetic components of circadian rhythms further emphasize the need for personalized approaches to managing insomnia and related mental health conditions. As Forger notes, “This work shows a lot of promise for future findings,” suggesting that understanding the interplay between genetics, circadian rhythms, and mental health could lead to more effective interventions.
Genetic Factors in Insomnia and Circadian Rhythms
Exploration of Genetic Components Influencing Individual Responses to Day Length Changes
The intricate dance between our genetics and circadian rhythms is a fascinating area of study. The University of Michigan research delves into how genetic variations can influence individual responses to changes in day length. It turns out that some people are more sensitive to these changes due to their genetic makeup. This sensitivity can affect how well they adapt to the shifting daylight hours throughout the year. By understanding these genetic components, researchers hope to tailor interventions that can help individuals better manage their sleep patterns and overall well-being.
Impact of Genetic Variations on Insomnia and Circadian Alignment in Shift Workers
Shift workers often face unique challenges when it comes to aligning their sleep schedules with their circadian rhythms. The genetic variations identified in the study suggest that some individuals may struggle more than others with this alignment. For those with certain genetic predispositions, the disruption caused by irregular work hours can lead to insomnia and other sleep-related issues. This research highlights the importance of considering genetic factors when developing strategies to support shift workers in maintaining healthy sleep habits. Personalized approaches that take into account an individual’s genetic profile could be key to mitigating the adverse effects of shift work on sleep and health.
Research Methodology and Findings on Insomnia
Use of Wearable Health Devices to Study Sleep Patterns in Medical Residents
The University of Michigan study utilized wearable health devices, such as Fitbits, to gather sleep data from medical residents. These devices provided a wealth of information about the participants’ sleep patterns, offering insights into how their circadian rhythms were influenced by seasonal changes. The use of wearable technology allowed researchers to collect real-time data in a naturalistic setting, providing a comprehensive view of how sleep schedules varied across different seasons. This innovative approach underscores the potential of wearable devices in sleep research, offering a non-invasive and practical method for monitoring sleep behaviors.
Evidence Supporting the Seasonal Dependence of Circadian Rhythms and Its Implications for Insomnia
The findings from the study provide compelling evidence for the seasonal dependence of circadian rhythms. This seasonal tuning of our internal clocks has significant implications for understanding insomnia and other sleep disorders. By recognizing the role of natural light cycles in regulating sleep, researchers can develop more effective interventions for those struggling with insomnia. Aligning sleep schedules with natural circadian rhythms could improve sleep quality and overall health. For those interested in exploring more about insomnia and sleep strategies, the Insomnia Blog offers a wealth of resources and insights. Additionally, for those seeking a restful night’s sleep, the Sleep Sound Playlists provide soothing sounds to help ease the transition into slumber.
Sources:https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/05/250528132237.htm